Human Resources departments are the backbone of organizational success, yet measuring their impact can be challenging. That’s where HR KPIs come into play. These critical metrics help organizations track, measure, and improve their human capital management while demonstrating the tangible value HR brings to the business.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore essential HR KPI examples, provide actionable HR analytics KPI frameworks, and show you how to implement effective measurement systems that drive real results.
What Are HR KPIs?
KPI HR metrics are quantifiable measurements that evaluate how effectively your Human Resources department achieves its key business objectives. Unlike general business KPIs, HR-specific indicators focus on people-related outcomes that directly impact organizational performance, culture, and growth.
These metrics serve multiple purposes:
- Demonstrate HR’s strategic value to leadership
- Identify areas for improvement in people management
- Guide data-driven decision making
- Align HR initiatives with business goals
- Track progress toward organizational objectives
Why HR KPIs Matter Today?
The role of HR has evolved dramatically from administrative support to strategic business partnership. Modern KPI in HR measurement helps organizations navigate challenges like talent shortages, remote work dynamics, and changing employee expectations.
Key benefits of implementing robust HR metrics include:
Strategic Alignment: HR KPIs ensure people strategies support overall business objectives, creating measurable connections between human capital investments and organizational outcomes.
Performance Optimization: Regular monitoring of HR department KPI examples reveals bottlenecks and opportunities, enabling continuous improvement in processes and programs.
Resource Allocation: Data-driven insights help HR leaders make informed decisions about budget allocation, staffing needs, and program investments.
Stakeholder Communication: Concrete metrics provide compelling evidence of HR’s contribution during board meetings, budget discussions, and strategic planning sessions.
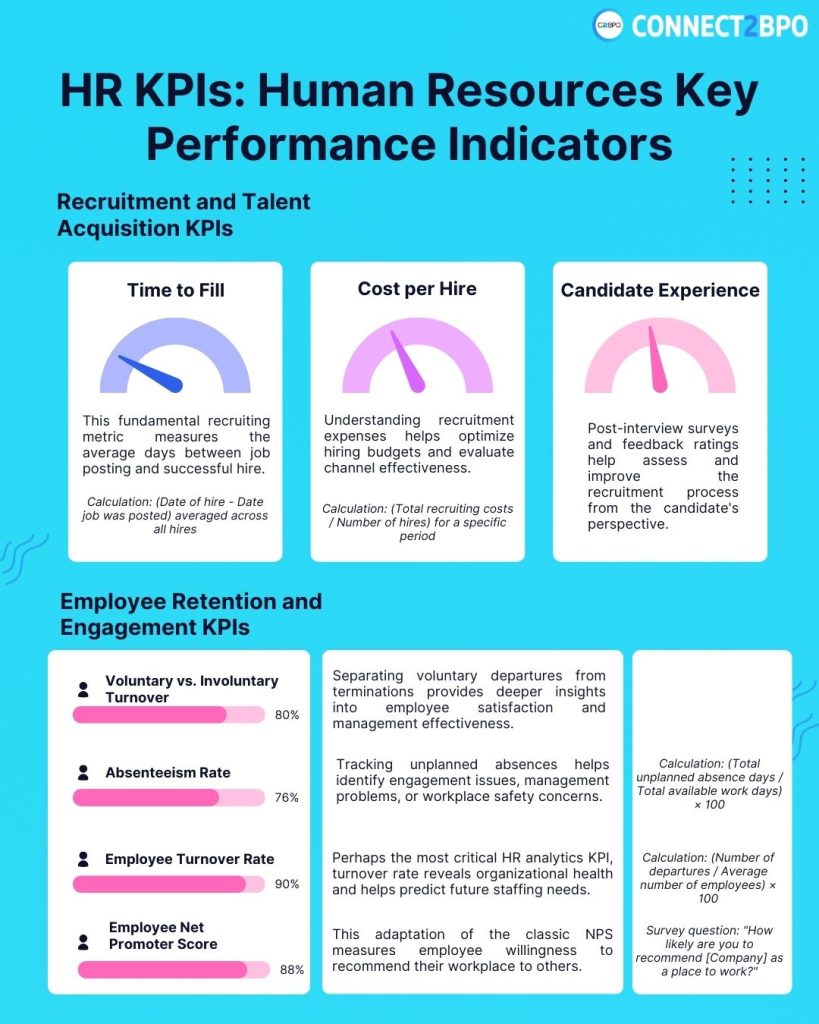
Essential HR KPI Categories
Recruitment and Talent Acquisition KPIs
Time to Fill This fundamental recruiting metric measures the average days between job posting and successful hire. Industry benchmarks vary, but most organizations aim for 30-45 days for standard positions.
Calculation: (Date of hire – Date job was posted) averaged across all hires
Cost per Hire Understanding recruitment expenses helps optimize hiring budgets and evaluate channel effectiveness.
Calculation: (Total recruiting costs / Number of hires) for a specific period
Quality of Hire This composite metric evaluates new employee performance, retention, and cultural fit during their first year.
Measurement approach: Combine performance ratings, retention rates, and manager satisfaction scores
Candidate Experience Score Post-interview surveys and feedback ratings help assess and improve the recruitment process from the candidate’s perspective.
Employee Retention and Engagement KPIs
Employee Turnover Rate Perhaps the most critical HR analytics KPI, turnover rate reveals organizational health and helps predict future staffing needs.
Calculation: (Number of departures / Average number of employees) × 100
Voluntary vs. Involuntary Turnover Separating voluntary departures from terminations provides deeper insights into employee satisfaction and management effectiveness.
Employee Net Promoter Score (eNPS) This adaptation of the classic NPS measures employee willingness to recommend their workplace to others.
Survey question: “How likely are you to recommend [Company] as a place to work?”
Absenteeism Rate Tracking unplanned absences helps identify engagement issues, management problems, or workplace safety concerns.
Calculation: (Total unplanned absence days / Total available work days) × 100
Performance and Productivity KPIs
Employee Productivity Metrics While challenging to measure universally, productivity indicators should align with specific role requirements and organizational goals.
Examples: Sales per employee, projects completed per team member, customer satisfaction scores by department
Performance Review Completion Rate This administrative metric ensures consistent performance management across the organization.
Goal Achievement Rate Tracking how often employees meet or exceed their objectives provides insights into goal-setting effectiveness and employee capability.
Training Completion Rate Monitoring learning and development participation helps assess employee engagement and skill development progress.
Compensation and Benefits KPIs
Compensation Ratio Comparing employee salaries to market rates helps maintain competitive positioning and identify pay equity issues.
Calculation: (Employee salary / Market median salary) × 100
Benefits Utilization Rate Understanding which benefits employees actually use helps optimize offerings and control costs.
Pay Equity Analysis Regular analysis of compensation across demographic groups ensures fair and legal pay practices.
Industry-Specific HR KPI Examples
Technology Companies
- Developer productivity metrics
- Innovation index scores
- Technical skill acquisition rates
- Remote work effectiveness measures
Healthcare Organizations
- Staff certification maintenance rates
- Patient satisfaction correlation with staffing levels
- Compliance training completion
- Burnout and wellness indicators
Retail Operations
- Seasonal staffing efficiency
- Customer service training effectiveness
- Loss prevention training impact
- Flexible scheduling satisfaction
Manufacturing
- Safety incident rates
- Skills training completion
- Cross-training effectiveness
- Shift efficiency metrics
HR Manager KPI Examples for Different Levels
Entry-Level HR Professionals
- Administrative task completion rates
- Response time to employee inquiries
- Data accuracy in HRIS systems
- Policy distribution and acknowledgment rates
HR Manager KPI Examples
- Team productivity improvements
- Employee satisfaction scores for HR services
- Project completion within budget and timeline
- Stakeholder satisfaction ratings
Senior HR Leadership
- Organizational culture assessment scores
- Strategic initiative implementation success
- Talent pipeline strength indicators
- HR technology ROI measurements
Building Your HR Analytics KPI Dashboard
Data Collection Best Practices
Automate Where Possible: Leverage HRIS systems, performance management platforms, and survey tools to reduce manual data entry and improve accuracy.
Establish Baseline Metrics: Before implementing new programs or processes, capture current performance levels to measure improvement accurately.
Ensure Data Quality: Regular audits of data sources and collection methods prevent skewed results and maintain credibility.
Visualization and Reporting
Executive Dashboards: Create high-level summaries focusing on metrics that directly impact business outcomes and strategic objectives.
Operational Reports: Develop detailed analytics for HR team members who need granular data for day-to-day decision making.
Trend Analysis: Historical data comparison reveals patterns and helps predict future challenges or opportunities.
Implementing HR KPIs: A Step-by-Step Approach
Phase 1: Assessment and Planning
- Review organizational goals and HR strategy alignment
- Identify key stakeholders and their information needs
- Audit current data collection capabilities
- Select initial HR KPI sample metrics for pilot implementation
Phase 2: Infrastructure Development
- Establish data collection processes and systems
- Create reporting templates and dashboards
- Train team members on new measurement approaches
- Develop communication plans for sharing results
Phase 3: Launch and Refinement
- Begin regular data collection and analysis
- Gather feedback from stakeholders on report usefulness
- Adjust metrics based on changing business needs
- Expand measurement scope as capabilities mature
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Measuring Everything: Focus on metrics that drive actionable insights rather than collecting data for its own sake. Too many KPIs can overwhelm stakeholders and dilute focus.
Ignoring Context: Raw numbers without context can be misleading. Always provide benchmarks, trends, and explanatory factors alongside your metrics.
Static Metrics: Business needs evolve, and your KPI for HR measurement should adapt accordingly. Regular reviews ensure continued relevance.
Lack of Action: Collecting data without using insights to drive improvements wastes resources and undermines credibility.
Advanced HR Analytics Techniques
Predictive Analytics
Moving beyond historical reporting, predictive models help forecast turnover risks, identify high-potential employees, and anticipate staffing needs.
People Analytics Integration
Combining HR metrics with business performance data reveals correlations and causations that drive strategic decision making.
Benchmarking and Industry Comparison
Regular comparison with industry standards and peer organizations provides context for performance evaluation and goal setting.
Technology Solutions for HR KPI Tracking
HRIS Integration
Modern Human Resource Information Systems offer built-in analytics capabilities that automatically calculate many standard HR metrics.
Specialized Analytics Platforms
Dedicated people analytics tools provide advanced visualization, predictive modeling, and benchmarking capabilities, like Gusto.
Survey and Feedback Tools
Regular pulse surveys and feedback collection systems provide real-time insights into employee sentiment and engagement.
Measuring ROI of HR Initiatives
Connecting HR KPIs to financial outcomes demonstrates clear value to organizational leadership:
Training ROI: Compare training costs to productivity improvements and retention benefits
Recruitment Efficiency: Analyze cost savings from improved hiring processes and reduced turnover
Employee Engagement Impact: Correlate engagement scores with customer satisfaction, sales performance, and profitability
Future Trends in HR KPIs
Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Metrics
Organizations increasingly focus on DEI indicators that track representation, pay equity, and inclusive culture development.
Remote Work Analytics
New metrics emerging around distributed team effectiveness, virtual collaboration quality, and work-life balance in hybrid environments.
Employee Wellbeing Indicators
Mental health metrics, stress indicators, and wellness program effectiveness become central to modern HR measurement.
Conclusion
Effective HR KPI implementation transforms human resources from a cost center into a strategic business driver. By selecting the right metrics, implementing robust measurement systems, and consistently acting on insights, HR professionals can demonstrate clear value while improving organizational performance.
The key to success lies in starting with a focused set of metrics aligned with business objectives, building reliable data collection processes, and continuously refining your approach based on stakeholder needs and changing business requirements.
Remember that the most sophisticated HR analytics KPI system is only valuable if it drives better decision making and improved outcomes for both employees and the organization. Focus on actionable insights rather than impressive dashboards, and you’ll build a measurement framework that truly supports your strategic HR goals.
Ready to implement comprehensive KPI tracking across your entire organization? Learn about essential business metrics and measurement frameworks in our complete guide to Key Performance Indicators.